FAQ about hot surface ignitor
In this post, as a manufacturer of ceramic hot surface ignitor, we will try to answer to most common question regarding hot surface ignitor.
What is a hot surface igniter?
A silicon nitride hot surface igniter is a device to light gas in gas burner, gas furnace or gas boiler appliances.
Hot surface ignitor are the most commonly used electronic ignition system. It works like a light bulb filament, heating up when electricity is passed through it. Most are made from silicon nitride or silicon carbide ceramic. When the gas valve opens, the gas is ignited by the igniter.
How work a hot surface igniter?
A spark plug or ignition electrode ignite gas by creating sparks (=electrical discharge). The intense heat of the spark causes the ionized gas to expand very quickly, like a small explosion and ignite the gas.
A hot surface ignitor work very differently. Electric current applied through a thermal resistance that create enough heat on the surface of the igniter (1100~1400°C) to make the gas auto-ignite.
How work a hot surface ignitor?
A heating element converts electrical energy into heat through the process of Joule heating (same principe that make incandescent light bulb glows). Electric current through the element encounters resistance, resulting in heating of the element.
Silicon nitride ceramic hot surface ignitor are PTC ceramic elements: PTC ceramic materials are named for their positive thermal coefficient of resistance (i.e., resistance increases upon heating). That mean that they have a highly nonlinear thermal response, so that above a composition-dependent threshold temperature their resistance increases rapidly. This behavior causes the material to act as its own thermostat, since current passes when it is cool, and does not when it is too hot, so the temperature stabilize at a certain tempereture (1100~1400°C).
How do I know if my hot surface ignitor is bad? How do you test a hot surface ignitor?
As a hot surface igniter is a resistance (thermal resistance producing heat), the only way to check if an ignitor is bad or broken is to check the resistance value.
You will need to use a ohmeter or multimeter to measure the cold resistance (when off) value of the igniter. Set the multimeter so it can properly measure a resistance of 10 to 200 ohms (at room temprature 21~23°C). Disconnect the hot surface ignitor from the control board and measure the resistance at the two electrodes (no polarity). A good silicon nitride hot surface ignitor will have a resistance of 30 to 75 ohms. Greater than 75 ohms indicates a failing or failed hot surface ignitor. If you get 0 or ∞ or no reading at all, it mean that the resistance is broken, so the igniter is broken and should be replaced.
How do you replace a hot surface ignitor?
Every appliances, furnace and burner are different. Please consult the appliance manual or call a professional to do the replacement.
What causes hot surface ignitor failure?
The lifespan of a ceramic ignitor depends mainly on two factors: time of use (or number of ignition) and surface temperature.
If the ignitor stays on for an extended period of time this will make the ignitor short-lived. Most of the time when ignitors go bad that often it is because the ignitor is not shutting off after the gas in the furnace is ignited. If the ignitor stays on for an extended period of time this will make the ignitor short-lived.
Also the highest is the surface temperature (depend on voltage applied), the shorter the lifespan will be.
From a professional and technical point of view, here are the main reason of ceramic hot surface degradation:
- Ionic migration (Chemical degradation, through oxidation of Si3N4 to SiO2, and reduction of the protective SiO2; migration of the sintering additive ions toward the surface) = reactions with the impurities in combustion gases or DC current (dielectric breakdown of Si3N4 across the resistors).
- Mechanical degradation: erosion by the high-pressure high-velocity combustion gases (very rare case).
- Thermal degradation: increased temperature increases the rate of chemical reactions at an exponential rate and is accelerated by the electrical degradation of the conductive phase.
How long should Furnace Ignitor last?
It depend on the appliances, number of ignition and temperature, but silicon nitride igniter have an average lifespan of 7 to 15 years.
Can you clean a hot surface ignitor?
It is not necessary to clean a hot surface igniter as it blow off any dust.
However contrary to silicon carbide ceramic hot surface ignitor which are very brittle and shouldn't be touched, silicon nitride hot surface ignitor are very robust and can be cleaned manually iff really necessary. If you can disassemble the igniter from appliance, clean the surface with a the toothbrush or dry cloth and do not use detergent. Make sure that the main power is off when cleaning the surface of the ignitor.
How do I clean the igniter on my furnace?
Insert the straw taped to the side of the can of compressed air into the nozzle of the can. Hold the can upright 12 inches from the ceramic ignitor. Tap the release button on the can to send a few short bursts of air onto the ignitor to clean away any dust.
How much current does a hot surface igniter use?
It depends on the igniter size and resistance.
Our 120 volts models have an average amperage of 0.4 to 0.6 Amps after stabilization and 2 to 4 Amps during rising temperature phase.
What are hot surface igniter made of?
The two composition materials generally associated with hot surface igniters are silicon carbide and silicon nitride. Silicon carbide is a compound of carbon and silicon and is characterized by a low density and oxidation resistance.
Are furnace ignitors universal?
Over the past several years, new style Silicon Nitride igniters for furnaces and boilers have taken over the industry. Virtually all new residential gas furnaces now feature this new type of igniter.
When should I replace my furnace ignitor?
Silicon nitride ignitors have an average lifespan of 7 to 15 years. So, after about 7 years, you may have to replace the ignitor.
Where are the silicon nitride igniter used?
Silicon nitride hot surface igniters are commonly used in various heating systems and appliances, particularly in applications that require reliable and efficient ignition of fuel or heating elements. Some of the specific applications where silicon nitride hot surface igniters are utilized include:
Gas Furnaces: Silicon nitride igniters are widely used in gas-fired furnaces. They provide a consistent and robust ignition source for igniting the gas burners, initiating the combustion process, and heating the furnace. Silicon nitride igniters are favored for their durability, high-temperature resistance, and quick heating capabilities.
Boilers: Boilers, whether used for residential heating or industrial processes, often incorporate silicon nitride hot surface igniters. These igniters efficiently ignite the fuel source, such as natural gas or oil, in the boiler's combustion chamber, ensuring reliable and efficient operation.
Water Heaters: Silicon nitride igniters are employed in gas-fired water heaters to ignite the gas burners that heat the water. The quick heating response and robust nature of silicon nitride make it a suitable choice for this application.
Ovens and Cooktops: In gas ovens and cooktops, silicon nitride igniters are used to ignite the gas burners for cooking or baking purposes. These igniters provide a safe and consistent ignition source, enabling precise temperature control and efficient cooking performance.
Industrial Heating Systems: Silicon nitride hot surface igniters find application in various industrial heating systems, including infrared heaters, industrial furnaces, and heat treatment equipment. They play a crucial role in initiating combustion processes, ensuring efficient heat transfer, and maintaining stable and controlled operating conditions.
Silicon nitride igniters are preferred over traditional silicon carbide igniters in many cases due to their faster heating response, longer lifespan, and higher temperature capabilities. However, the specific application and requirements of the heating system or appliance will determine the most suitable type of igniter to use.
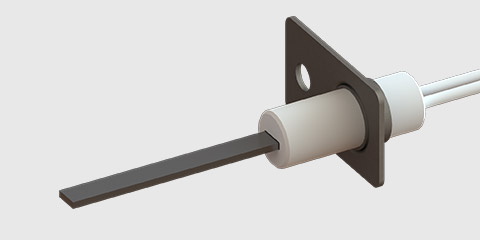
What does a furnace ignitor look like?
Common silicon nitride hot surface ignitor looks like the picture below.